Inventory control refers to the process of managing and regulating the flow of goods in a business. It involves keeping track of inventory levels, monitoring sales trends, and determining when and how much to order. Effective inventory control can help businesses reduce costs, improve customer service, and increase profits. In this article, we will discuss the ways in which businesses can implement inventory control.
Accurate Record Keeping: One of the key components of inventory control is accurate record keeping. This involves keeping track of inventory levels, sales data, and ordering information. With accurate record keeping, businesses can make informed decisions about when and how much to order, and can avoid stock outs and overstocking.
Automated Systems: Many businesses use automated inventory control systems to streamline their operations. These systems can track inventory levels, monitor sales data, and even place orders automatically. By using automated systems, businesses can save time and reduce errors.
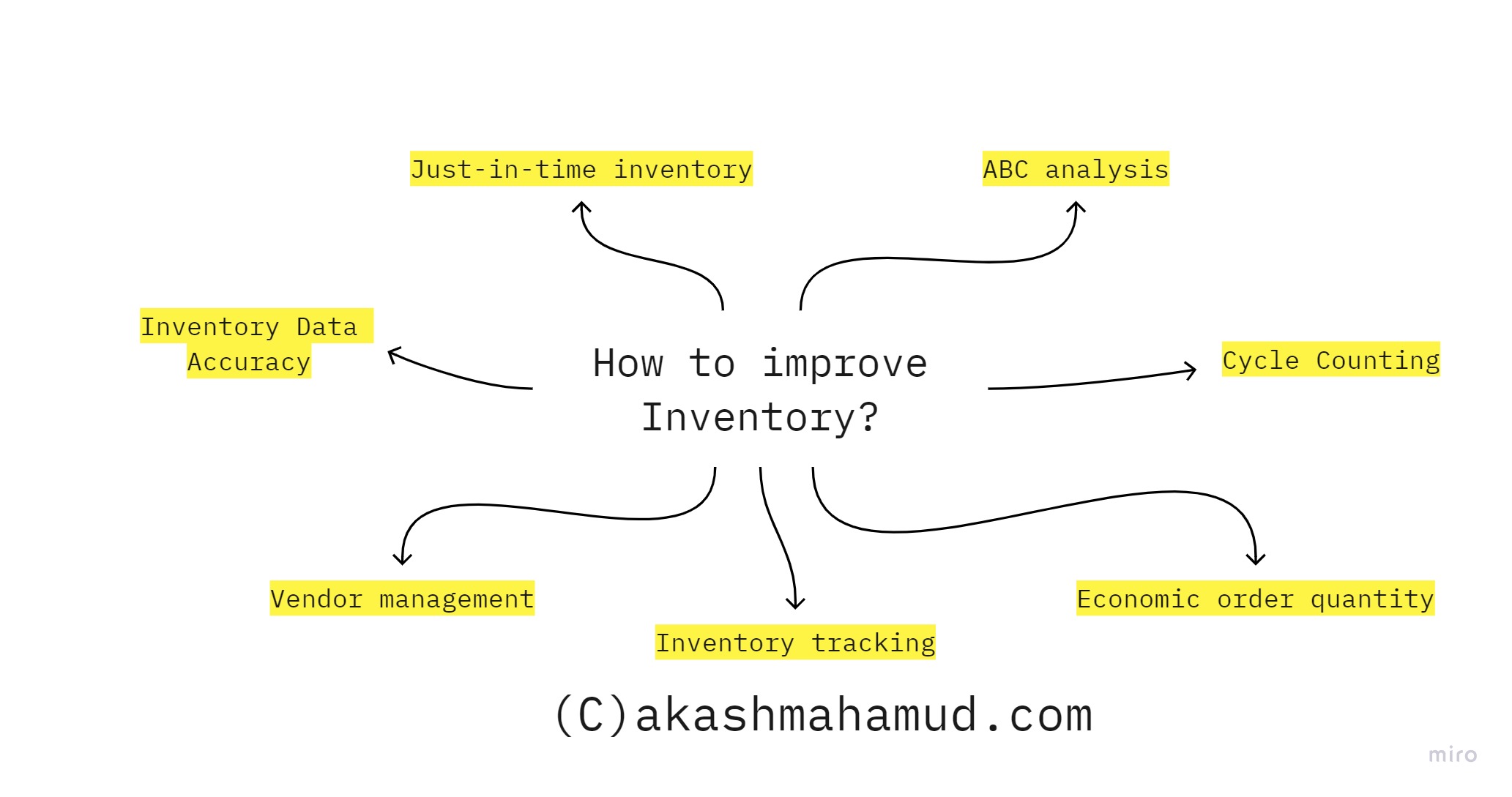
Just-in-Time Inventory: Just-in-time inventory is a system in which businesses only order what they need, when they need it. This can help businesses reduce costs by minimizing the amount of inventory they need to hold, and can also improve customer service by ensuring that products are always in stock.
ABC Analysis: ABC analysis is a method of inventory control that involves categorizing inventory items based on their importance. High-value items that sell quickly are given a higher priority than low-value items that sell slowly. By focusing on high-priority items, businesses can ensure that they always have enough inventory to meet demand.
Regular Audits: Regular inventory audits can help businesses identify problems with their inventory control systems. By conducting audits on a regular basis, businesses can identify discrepancies between their records and actual inventory levels, and can take corrective action as needed.
Vendor Management: Effective vendor management is another key component of inventory control. By building strong relationships with vendors, businesses can negotiate better prices, improve delivery times, and ensure that they always receive high-quality products.
In conclusion, effective inventory control is essential for businesses of all sizes. By implementing accurate record keeping, automated systems, just-in-time inventory, ABC analysis, regular audits, and effective vendor management, businesses can reduce costs, improve customer service, and increase profits.